I recently used a thermal camera during a home inspection, and it was impressive how easily it detected hidden heat leaks. The thermal camera helped me spot issues I couldn’t see with the naked eye, saving both time and repair costs.
A thermal camera detects heat signatures and converts them into visible images, making it easy to see temperature differences. Whether for security, inspections, or night vision, a thermal camera provides clear visuals even in complete darkness.
In this article we discuss “Thermal Camera“
Table of Contents
Thermal Camera: The Complete Guide to Heat-Based Imaging:
What Is a Thermal Camera?
A thermal camera is a type of specialized imaging equipment that creates a visible image by detecting heat, or infrared radiation, from objects. Thermal cameras operate in complete darkness, through smoke, fog, and other difficult situations, in contrast to conventional cameras that depend on visible light to create an image.
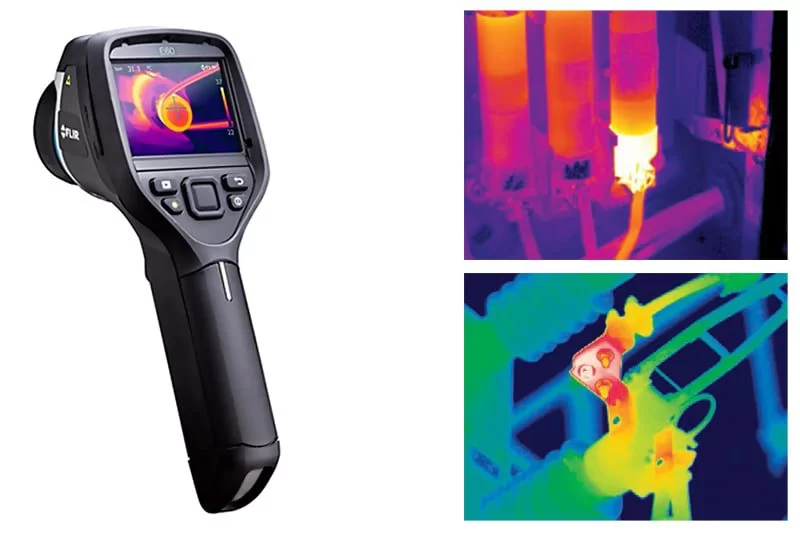

Infrared radiation is released by every item that has a temperature higher than absolute zero, and thermal cameras allow the human eye to see this invisible energy.
This technology is widely used in security, industrial inspection, firefighting, search and rescue, and even wildlife observation. Whether you are monitoring critical infrastructure or ensuring perimeter security, a thermal camera offers a level of visibility unmatched by traditional cameras.
How Thermal Cameras Work:
The central component of a thermal camera is a sensor that detects infrared radiation. When the infrared energy of an item hits the camera’s detector, an electronic signal is produced.. After processing, this signal is shown as a thermogram, which is a color-coded picture in which various hues correspond to various temperatures.
For example, cooler regions are depicted in blue or purple, whereas warmer objects may be brightly colored in red, orange, and yellow. In contrast to night vision equipment that needs some ambient light, thermal cameras work flawlessly in total darkness. They show temperature variations that might be imperceptible to the human eye in addition to capturing forms.
Key Benefits of Thermal Cameras:
Thermal cameras offer several benefits across various sectors:
- 24/7 Visibility – They operate equally well during the day or night.
- Non-Contact Measurement – Detect temperatures without touching the object.
- Through-Hazard Vision – See through smoke, light fog, or foliage.
- Privacy-Friendly Surveillance – No personal identification, making them compliant with privacy laws.
- Preventive Safety – Detect overheating, leaks, or potential hazards before they escalate.
These benefits make them indispensable in areas like security, firefighting, and predictive maintenance.
Industrial Applications of Thermal Cameras:
In the industry, downtime can be costly. Thermal cameras identify issues early on, preventing unplanned malfunctions. For instance, in electrical systems, a loose connection might heat up before failing. A thermal camera can spot this “hot spot” before it causes a power outage or fire.
They are also used in:
- Oil and Gas – Inspecting pipelines for leaks.
- Manufacturing – Monitoring machinery temperature to avoid overheating.
- Construction – Identifying insulation gaps and energy losses in buildings.
- Renewable Energy – Checking solar panels for faulty cells or wiring.
The result is not just better safety, but also significant cost savings.
Security and Surveillance with Thermal Cameras:
When it comes to security, visibility is everything. A thermal camera can detect intruders hiding in shadows or behind light vegetation, making it an essential tool for perimeter protection, border security, and facility monitoring.
They excel in environments where conventional cameras struggle, such as unlit areas or extreme weather conditions. Importantly, because they capture heat signatures rather than visual identities, thermal cameras respect privacy while still providing reliable detection.
Temperature Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance:
Software that enables users to adjust temperature thresholds is frequently included with contemporary thermal cameras.When an object’s temperature exceeds that threshold, the camera sends an alert — either via email, text, or an integrated monitoring system.
This feature is especially valuable for:
- Factory equipment monitoring
- Electrical grid maintenance
- HVAC system performance checks
- Data center cooling efficiency
Businesses can save time and money by performing maintenance before issues arise, allowing them to address problems early.
Types of Thermal Cameras:

There are various types of thermal cameras, and each is appropriate for a particular use case:
- Field inspections benefit greatly from the portability of handheld thermal cameras.
- Fixed-Mount Thermal Cameras – Installed for continuous monitoring in factories or security systems.
- Thermal Camera Modules – Built into other devices like drones or smartphones for specialized use.
The right type depends on whether you need mobility, wide coverage, or permanent monitoring.
Choosing the Right Thermal Camera:
Selecting the best thermal camera for your needs requires evaluating several factors:
- Resolution: Thermal images with a higher resolution are crisper and more detailed.
- The lower the thermal sensitivity number, the smaller the temperature differential the camera can detect.
- Field of View (FOV) – A wider FOV captures more area, useful for security applications.
- Temperature Range – Important for extreme heat or cold environments.
- Durability – Check IP (Ingress Protection) and IK (impact resistance) ratings for harsh environments.
For example, a construction inspector might need high resolution and portability, while a security firm may prioritize wide coverage and weather resistance.
Thermal Cameras vs. Infrared Thermometers:
They both detect infrared radiation, but they serve different purposes. An infrared thermometer is ideal for fast checks because it only detects temperature at one location. In contrast, a thermal camera records a whole heat map, which lets you observe temperature changes over a whole surface or area.
In short, if you need detailed imaging and broad area coverage, a thermal camera is the better choice.
The Future of Thermal Imaging:
The development of AI and sensor technologies has led to a rapid evolution in thermal imaging. Thermal cameras of the future will be more compact, less expensive, and able to recognize objects automatically.
Emerging trends include:
- Integration with drones for large-area surveillance.
- AI-driven analytics for faster decision-making.
- Smart building integration for energy efficiency.
- Wearable thermal equipment for rescuers and field technicians.
As these innovations continue, thermal cameras will become even more valuable across industries, making heat-based imaging an essential part of modern technology.
Final Thoughts:
Whether for security, industrial inspection, or scientific research, a thermal camera provides unparalleled insight into the world of heat. Its ability to detect temperature differences in real-time can prevent accidents, improve efficiency, and offer security in challenging environments. With technology advancing rapidly, owning a thermal camera has never been more accessible or more beneficial.
Thermography Certification:
A thermal camera is a kind of specialized imaging device that uses heat, or infrared radiation, from objects to produce a visible image.Thermal cameras operate in complete darkness, through smoke, fog, and other difficult situations, in contrast to conventional cameras that depend on visible light to create an image. Infrared radiation is released by every item that has a temperature higher than absolute zero, and thermal cameras allow the human eye to see this invisible energy.
Handheld Thermal Cameras:
Handheld thermal cameras are portable devices that detect heat and convert it into clear thermal images, making them perfect for inspections, security, and maintenance tasks.

With a handheld thermal camera, you can quickly identify heat leaks, electrical faults, or hidden issues even in complete darkness.
Infrared Thermal Imaging Camera:
An infrared thermal imaging camera detects heat signatures and converts them into clear, visible images, making it easy to spot temperature differences. Whether for inspections, security, or maintenance, an infrared thermal imaging camera works perfectly even in total darkness or challenging conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. Can I use my phone as a thermal camera?
Yes, but only with a special thermal camera attachment like FLIR or Seek Thermal. These plug into your phone and allow it to detect heat signatures.
2. Is it legal to own a thermal camera?
Yes, owning a thermal camera is legal in most countries. However, exporting high-end models may be restricted due to military-grade technology.
3. What is the difference between an infrared camera and a thermal camera?
Infrared cameras detect reflected infrared light, while thermal cameras detect emitted heat. Thermal cameras are better for detecting temperature differences in complete darkness.
4. Can a thermal camera see through a house?
No, thermal cameras cannot see through walls or solid objects. They only detect surface temperatures.
5. Do bugs show up on thermal cameras?
Yes, larger insects like bees or wasps may appear on thermal cameras if there’s enough temperature contrast with their surroundings.
6. How can I tell if a hidden camera is in my room?
Look for unusual objects, use a flashlight to spot lens reflections, or use RF detectors or hidden camera apps to scan for signals.
7. Can a phone detect a hidden camera?
Yes, some apps help detect hidden cameras using your phone’s magnetometer or camera to find lens reflections or unusual RF signals.
8. Are hidden cameras legal everywhere?
No, laws vary by location. Hidden cameras are usually legal in public or common areas but illegal in private spaces like bathrooms or bedrooms without consent.
9. How to tell if your TV has a hidden camera?
Check the bezel or top edge for small lens holes or use a flashlight to spot any unusual reflections. Also, review the TV’s privacy settings and specs.
10. Can someone watch you through your smart TV?
Yes, if your smart TV has a camera and it’s hacked or poorly secured, someone could potentially access it. Always update firmware and disable unused features.
Conclusion:
A thermal camera is more than just a heat-detecting device — it’s a powerful tool for safety, efficiency, and problem-solving across countless industries. From spotting hidden faults to enhancing security in complete darkness, its ability to visualize temperature differences gives you insights no regular camera can. With advancing AI, portability, and affordability, thermal imaging is becoming an essential everyday technology. Investing in the right thermal camera today means being prepared for a smarter, safer, and more efficient future.